“MMC overview”的版本间的差异
Zhouyuebiao(讨论 | 贡献) |
Zhouyuebiao(讨论 | 贡献) |
||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| − | + | '''SUMMARY '''<br> | |
| + | The MMC (MultiMediaCard) / SD (secure digital) / SDIO (secure digital input/output) subsystem implements a standard Linux<sup>®</sup> host driver to interface with MMC / SD memory cards or SDIO cards. | ||
| − | [[ | + | == Framework purpose == |
| − | + | The purpose of this article is to introduce the MMC Linux<sup>®</sup> subsystem (MMC / SD) by: | |
| − | + | * providing general information | |
| + | * describing the main components/stakeholders | ||
| + | |||
| + | The SDIO is addressed in the [[WLAN_overview|WLAN overview]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==System overview== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:MMC_overview.png|center|link=]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Component description=== | ||
| + | * User space applications handle '''file I/O''' management to view the card memory as a disk, whereas programs that perform '''raw I/O''' accesses see the memory as a block device<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file#Block_devices</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''VFS''' (Kernel space) | ||
| + | Virtual File System. Please refer to the VFS documentation <ref>{{CodeSource | Linux kernel | Documentation/filesystems/vfs.txt | VFS}} </ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''MMC core/SD/MMC/SDIO''' (Kernel space) | ||
| + | The '''MMC core''' ensures compliance with MultiMediaCard ('''MMC''')<ref>[https://www.jedec.org/standards-documents/technology-focus-areas/flash-memory-ssds-ufs-emmc/e-mmc MultiMediaCard], embedded MultiMediaCard specification</ref> / secure digital ('''SD''')<ref>[https://www.sdcard.org/ Secure Digital], secure digital specification</ref> / secure digital input/output ('''SDIO''')<ref>[https://www.sdcard.org/ Secure Digital Input Output], Secure Digital Input Output specification</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''SDMMC driver''' (Kernel space) / '''SDMMC''' (hardware) | ||
| + | The '''SDMMC driver''' handles: | ||
| + | * the registers, the clock, the interrupt and the IDMA control. | ||
| + | * the communications over the bus based on command/response and data transfers. | ||
| + | Please refer to the [[SDMMC internal peripheral]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===API description=== | ||
| + | The MMC core handles the file system read/write calls. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Configuration == | ||
| + | ===Kernel configuration=== | ||
| + | The MMC framework is activated by default in ST deliveries. If a specific configuration is needed, this section indicates how the MMC framework can be activated/inactivated in the kernel. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The MMC framework can be activated in the kernel configuration via Linux<sup>®</sup> Menuconfig tool: [[Menuconfig or how to configure kernel]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | [*] Device Drivers | ||
| + | [*] MMC/SD/SDIO card support | ||
| + | <*> HW reset support for eMMC | ||
| + | <*> Simple HW reset support for MMC | ||
| + | <*> MMC block device driver | ||
| + | (16) Number of minors per block device | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | <*> ARM AMBA Multimedia Card Interface support | ||
| + | [*] STMicroelectronics STM32 SDMMC Controller | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Device tree configuration=== | ||
| + | DT configuration can be done thanks to [[STM32CubeMX]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Please refer to the [[SDMMC_device_tree_configuration| SDMMC device tree configuration]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==How to use the framework== | ||
| + | A file system, which handles read/write/erase operations, can be used with the MMC framework. Please refer to the [[How to support EXT4 through MMC|EXT4 support through MMC]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==How to trace and debug the framework== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===How to monitor=== | ||
| + | The sysfs interface provides detailed information on each mmc device: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | root:~# cat /sys/kernel/debug/mmc0/ios | ||
| + | clock: 50000000 Hz | ||
| + | vdd: 21 (3.3 ~ 3.4 V) | ||
| + | bus mode: 2 (push-pull) | ||
| + | chip select: 0 (don't care) | ||
| + | power mode: 2 (on) | ||
| + | bus width: 2 (4 bits) | ||
| + | timing spec: 2 (sd high-speed) | ||
| + | signal voltage: 0 (3.30 V) | ||
| + | driver type: 0 (driver type B) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===How to trace=== | ||
| + | For details on dynamic trace usage, refer to [[How to use the kernel dynamic debug]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | root:~# echo "file drivers/mmc/* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Source code location== | ||
| + | The MMC framework is available {{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/mmc | here}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | Please refer to the following links for a full description of the MMC framework: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <noinclude> | ||
| + | {{ArticleBasedOnModel | Framework overview article model}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Mass storage]] | ||
| + | </noinclude> | ||
2020年5月8日 (五) 22:17的版本
SUMMARY
The MMC (MultiMediaCard) / SD (secure digital) / SDIO (secure digital input/output) subsystem implements a standard Linux® host driver to interface with MMC / SD memory cards or SDIO cards.
目录
Framework purpose
The purpose of this article is to introduce the MMC Linux® subsystem (MMC / SD) by:
- providing general information
- describing the main components/stakeholders
The SDIO is addressed in the WLAN overview.
System overview
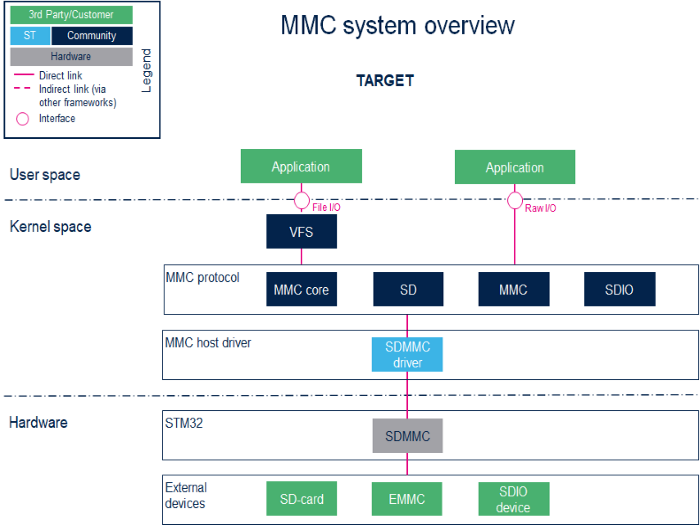
Component description
- User space applications handle file I/O management to view the card memory as a disk, whereas programs that perform raw I/O accesses see the memory as a block device[1].
- VFS (Kernel space)
Virtual File System. Please refer to the VFS documentation [2].
- MMC core/SD/MMC/SDIO (Kernel space)
The MMC core ensures compliance with MultiMediaCard (MMC)[3] / secure digital (SD)[4] / secure digital input/output (SDIO)[5].
- SDMMC driver (Kernel space) / SDMMC (hardware)
The SDMMC driver handles:
- the registers, the clock, the interrupt and the IDMA control.
- the communications over the bus based on command/response and data transfers.
Please refer to the SDMMC internal peripheral.
API description
The MMC core handles the file system read/write calls.
Configuration
Kernel configuration
The MMC framework is activated by default in ST deliveries. If a specific configuration is needed, this section indicates how the MMC framework can be activated/inactivated in the kernel.
The MMC framework can be activated in the kernel configuration via Linux® Menuconfig tool: Menuconfig or how to configure kernel
[*] Device Drivers
[*] MMC/SD/SDIO card support
<*> HW reset support for eMMC
<*> Simple HW reset support for MMC
<*> MMC block device driver
(16) Number of minors per block device
...
<*> ARM AMBA Multimedia Card Interface support
[*] STMicroelectronics STM32 SDMMC Controller
Device tree configuration
DT configuration can be done thanks to STM32CubeMX.
Please refer to the SDMMC device tree configuration.
How to use the framework
A file system, which handles read/write/erase operations, can be used with the MMC framework. Please refer to the EXT4 support through MMC.
How to trace and debug the framework
How to monitor
The sysfs interface provides detailed information on each mmc device:
root:~# cat /sys/kernel/debug/mmc0/ios clock: 50000000 Hz vdd: 21 (3.3 ~ 3.4 V) bus mode: 2 (push-pull) chip select: 0 (don't care) power mode: 2 (on) bus width: 2 (4 bits) timing spec: 2 (sd high-speed) signal voltage: 0 (3.30 V) driver type: 0 (driver type B)
How to trace
For details on dynamic trace usage, refer to How to use the kernel dynamic debug.
root:~# echo "file drivers/mmc/* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
Source code location
The MMC framework is available drivers/mmc | |}} here .
References
Please refer to the following links for a full description of the MMC framework:
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file#Block_devices
- ↑ Documentation/filesystems/vfs.txt | |}} VFS
- ↑ MultiMediaCard, embedded MultiMediaCard specification
- ↑ Secure Digital, secure digital specification
- ↑ Secure Digital Input Output, Secure Digital Input Output specification
<securetransclude src="ProtectedTemplate:ArticleBasedOnModel" params="Framework overview article model"></securetransclude>