“USB overview”的版本间的差异
| (未显示同一用户的13个中间版本) | |||
| 第70行: | 第70行: | ||
===Kernel configuration=== | ===Kernel configuration=== | ||
| − | + | 在ST交付中,默认情况下激活USB支持,[[USBH internal peripheral|STM32 USBH]] 驱动程序和[[OTG internal peripheral|STM32 OTG]] 驱动程序。 但是,如果需要特定的配置,则本节说明如何在内核中激活/停用USB框架。 | |
| − | + | 使用Linux Menuconfig工具在内核配置中激活USB支持(CONFIG_USB=y):[[Menuconfig or how to configure kernel]] | |
| − | + | 然后选择: | |
| − | |||
Device Drivers ---> | Device Drivers ---> | ||
[*] USB support ---> | [*] USB support ---> | ||
| − | + | 然后激活USB控制器驱动程序。 | |
| − | + | 要激活 [[USBH internal peripheral|STM32 USBH]] 驱动程序,请选择: | |
Device Drivers ---> | Device Drivers ---> | ||
--- USB support | --- USB support | ||
| 第86行: | 第85行: | ||
<*> OHCI HCD (USB 1.1) support | <*> OHCI HCD (USB 1.1) support | ||
<*> Generic OHCI driver for a platform device | <*> Generic OHCI driver for a platform device | ||
| − | + | 要激活 [[OTG internal peripheral|STM32 OTG]] 驱动程序,请选择: | |
Device Drivers ---> | Device Drivers ---> | ||
--- USB support | --- USB support | ||
| 第93行: | 第92行: | ||
<*> DesignWare USB2 DRD Core Support | <*> DesignWare USB2 DRD Core Support | ||
DWC2 Mode Selection (Dual Role mode) ---> | DWC2 Mode Selection (Dual Role mode) ---> | ||
| − | + | 然后,要激活[[USBPHYC internal peripheral|STM32 USBPHYC]] 驱动程序,请选择: | |
PHY Subsystem ---> | PHY Subsystem ---> | ||
-*- PHY Core | -*- PHY Core | ||
| 第99行: | 第98行: | ||
===Device tree configuration=== | ===Device tree configuration=== | ||
| − | + | STM32 USB内部外围设备的详细DT配置: | |
| − | * | + | * 用于[[USBH internal peripheral|STM32 USBH]] 主机控制器: [[USBH_device_tree_configuration | USBH device tree configuration]] |
| − | * | + | * 用于[[OTG internal peripheral|STM32 OTG]] 控制器:[[OTG_device_tree_configuration | OTG device tree configuration]] |
| − | * | + | * 用于 [[USBPHYC internal peripheral|STM32 USBPHYC]] PHY: [[USBPHYC_device_tree_configuration | USBPHYC device tree configuration]] |
==How to use the framework== | ==How to use the framework== | ||
===How to list USB devices=== | ===How to list USB devices=== | ||
| − | '''lsusb''' | + | '''lsusb'''显示有关所连接的USB总线和设备的信息。 <br /> |
| − | + | 在上面的示例中,我们有一个板载集线器,一个USB鼠标和USB键盘插入了该集线器。<br /> | |
{{Board$}} '''lsusb''' {{Highlight|/* '''root hubs''' correspond to STM32 USB controllers ([[USBH_internal_peripheral|USBH]], [[OTG_internal_peripheral| OTG]]) */}} | {{Board$}} '''lsusb''' {{Highlight|/* '''root hubs''' correspond to STM32 USB controllers ([[USBH_internal_peripheral|USBH]], [[OTG_internal_peripheral| OTG]]) */}} | ||
| 第123行: | 第122行: | ||
/: Bus 01.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=dwc2/1p, 480M | /: Bus 01.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=dwc2/1p, 480M | ||
| − | + | 要将'''lsusb'''限制为USB键盘: | |
{{Board$}} '''lsusb -s 002:005''' {{Highlight|/* '''lsusb -s [Bus]:[Device]''' */}} | {{Board$}} '''lsusb -s 002:005''' {{Highlight|/* '''lsusb -s [Bus]:[Device]''' */}} | ||
Bus 002 Device 005: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard | Bus 002 Device 005: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard | ||
| 第129行: | 第128行: | ||
Bus 002 Device 005: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard | Bus 002 Device 005: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard | ||
| − | + | 要将'''lsusb'''限制为USB键盘并显示其描述符: | |
{{Board$}} '''lsusb -D /dev/bus/usb/002/005''' {{Highlight|/* '''lsusb -D /dev/bus/usb/[Bus]/[Device]''' */}} | {{Board$}} '''lsusb -D /dev/bus/usb/002/005''' {{Highlight|/* '''lsusb -D /dev/bus/usb/[Bus]/[Device]''' */}} | ||
Device: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard | Device: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard | ||
| 第140行: | 第139行: | ||
===How to configure USB Gadget through configfs=== | ===How to configure USB Gadget through configfs=== | ||
| − | + | 请参阅[https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/usb/gadget_configfs.txt USB gadget configfs documentation] ,以获取USB gadget configfs结构的介绍以及如何使用它来配置Linux USB Gadget。 | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | 以下是通过配置文件配置USB Gadget以将OTG用作具有远程NDIS(RNDIS)的USB以太网Gadget的示例。 见: | |
[https://github.com/STMicroelectronics/meta-st-openstlinux/blob/thud/recipes-bsp/tools/usbotg-gadget-config/stm32_usbotg_eth_config.sh stm32_usbotg_eth_config.sh]. | [https://github.com/STMicroelectronics/meta-st-openstlinux/blob/thud/recipes-bsp/tools/usbotg-gadget-config/stm32_usbotg_eth_config.sh stm32_usbotg_eth_config.sh]. | ||
| 第149行: | 第150行: | ||
===How to monitor=== | ===How to monitor=== | ||
====How to monitor with debugfs==== | ====How to monitor with debugfs==== | ||
| − | + | 请参考[https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/driver-api/usb/usb.html#the-usb-devices the USB devices chapter]<ref>[https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/driver-api/usb/usb.html#the-usb-devices Linux USB API: The Linux-USB Host Side API - The USB devices]</ref> 对输出进行解码。 | |
{{Board$}} '''cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/devices''' | {{Board$}} '''cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/devices''' | ||
| 第204行: | 第205行: | ||
==== How to monitor with sysfs ==== | ==== How to monitor with sysfs ==== | ||
===== USB buses monitoring with sysfs ===== | ===== USB buses monitoring with sysfs ===== | ||
| − | + | 请参考[http://www.linux-usb.org/FAQ.html#i6 What are the sysfs structures for Linux USB?]<ref>[http://www.linux-usb.org/FAQ.html#i6 What are the sysfs structures for Linux USB?]</ref>. | |
{{Board$}} ls /sys/bus/usb/devices/ | {{Board$}} ls /sys/bus/usb/devices/ | ||
1-0:1.0 1-1 1-1:1.0 2-0:1.0 2-1 2-1.4 2-1.4:1.0 2-1:1.0 usb1 usb2 | 1-0:1.0 1-1 1-1:1.0 2-0:1.0 2-1 2-1.4 2-1.4:1.0 2-1:1.0 usb1 usb2 | ||
| − | + | 以“''usb''''开头的名称是指USB控制器。 | |
| − | + | 设备命名方案如下: | |
* bus-port{{Grey|.port}}{{Grey|.port...}} ('''1-1''', '''2-1''', or '''2-1.4''' in the example above) | * bus-port{{Grey|.port}}{{Grey|.port...}} ('''1-1''', '''2-1''', or '''2-1.4''' in the example above) | ||
| − | + | 这些接口由后缀表示,格式如下: | |
* :config.interface (1-1''':1.0''', 2-1''':1.0''', 2-1.4''':1.0''' in the example above) | * :config.interface (1-1''':1.0''', 2-1''':1.0''', 2-1.4''':1.0''' in the example above) | ||
| − | + | 每个接口对应于sysfs中的一个条目,并且可以具有自己的驱动程序。 | |
===== USB Gadget monitoring with sysfs ===== | ===== USB Gadget monitoring with sysfs ===== | ||
| − | + | 配置USB小工具后,将填充USB设备控制器sysfs。 参见 {{CodeSource | Linux kernel | Documentation/ABI/stable/sysfs-class-udc}} for a description of each file. | |
{{Board$}} ls /sys/class/udc/49000000.usb-otg/ | {{Board$}} ls /sys/class/udc/49000000.usb-otg/ | ||
a_alt_hnp_support device is_selfpowered srp | a_alt_hnp_support device is_selfpowered srp | ||
| 第228行: | 第229行: | ||
===How to trace=== | ===How to trace=== | ||
==== How to trace with usbmon ==== | ==== How to trace with usbmon ==== | ||
| − | usbmon <ref>{{CodeSource | Linux kernel | Documentation/usb/usbmon.txt | usbmon}}</ref> | + | usbmon <ref>{{CodeSource | Linux kernel | Documentation/usb/usbmon.txt | usbmon}}</ref> 收集USB总线上的输入/输出轨迹。<br/> |
| − | + | 它依赖于内核部分和用户部分,并将USB设备驱动程序发出的请求报告给主机控制器驱动程序。<br /> | |
| − | + | 使用Linux Menuconfig工具在[[Menuconfig or how to configure kernel]]内核配置中激活USBMON支持(CONFIG_USB_MON = y)。 <br /> | |
| − | + | 在debugfs中创建了一个usbmon条目。 它包括几个文件。<br /> | |
| − | + | 文件名由一个数字(USB总线-0表示所有总线)和一个字母(s,u或t)组成。 s文件包含通用事件概述。 t(不建议使用)和u文件将流跟踪数据。<br /> | |
| − | + | 要收集调试数据,请使用主文件0u(以从所有设备捕获数据)或找出设备所连接的总线并使用相应的总线文件。 例如,如果设备连接到总线1: | |
{{Board$}} cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/usbmon>1u > bus1data.log | {{Board$}} cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/usbmon>1u > bus1data.log | ||
| − | + | 要停止捕获,只需键入(CTRL + C)即可终止命令。 然后,您可以使用Linux主机上的 [http://vusb-analyzer.sourceforge.net/ vUSBAnalyzer] 图形工具来分析日志 | |
==== How to trace using a protocol analyzer ==== | ==== How to trace using a protocol analyzer ==== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | USB协议分析器是一种USB流量嗅探器,用于解码USB描述符并显示发送的总线状态和数据包。 请参阅您的USB协议分析器用户手册。 | ||
===How to debug=== | ===How to debug=== | ||
====Activating USB framework debug messages==== | ====Activating USB framework debug messages==== | ||
| − | + | 有关详细的动态跟踪信息,请参阅 [[How to use the kernel dynamic debug]]<br/> | |
{{Board$}} echo "file usb* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control | {{Board$}} echo "file usb* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control | ||
| − | + | 此命令在运行时启用与USB内核和驱动程序相关的所有跟踪。<br/> | |
| − | + | 通过仅选择要跟踪的文件,可以进行更精细的选择。<br/> | |
| − | {{Info| | + | {{Info|提醒:''loglevel''需要通过使用引导参数或从控制台发送''dmesg-n 8''命令增加到8}} |
==== EHCI/OHCI driver debugfs entry ==== | ==== EHCI/OHCI driver debugfs entry ==== | ||
| − | + | 启用CONFIG_DYNAMIC_DEBUG时,EHCI/uchI驱动程序会导出调试文件系统条目。 | |
{{Board$}} ls /sys/kernel/debug/usb/ohci/5800c000.usbh-ohci/ | {{Board$}} ls /sys/kernel/debug/usb/ohci/5800c000.usbh-ohci/ | ||
| − | + | 异步周期寄存器 | |
{{Board$}} ls /sys/kernel/debug/usb/ehci/5800d000.usbh-ehci/ | {{Board$}} ls /sys/kernel/debug/usb/ehci/5800d000.usbh-ehci/ | ||
| − | + | 异步带宽定期寄存器 | |
| − | * '''async''' | + | * '''async''' 转储异步计划的快照。 |
| − | * '''bandwith''' | + | * '''bandwith''' 转储带宽分配 |
| − | * '''periodic''' | + | * '''periodic''' 转储定期计划的快照。 |
| − | * '''registers''' | + | * '''registers''' 转储USB控制器寄存器 |
==== DWC2 driver debug messages and debugfs entry==== | ==== DWC2 driver debug messages and debugfs entry==== | ||
| − | + | 要从 [[OTG_internal_peripheral| STM32 OTG]],通过menuconfig[[Menuconfig or how to configure kernel]]在Linux内核中激活“启用调试消息”。<br/> | |
Device Drivers ---> | Device Drivers ---> | ||
[*] USB support | [*] USB support | ||
| 第270行: | 第272行: | ||
[ ] Enable Missed SOF Tracking | [ ] Enable Missed SOF Tracking | ||
[*] Enable Debugging Messages For Periodic Transfers | [*] Enable Debugging Messages For Periodic Transfers | ||
| − | + | 这可以在您的内核.config文件中手动完成: | |
CONFIG_USB_SUPPORT=y | CONFIG_USB_SUPPORT=y | ||
CONFIG_USB_DWC2=y | CONFIG_USB_DWC2=y | ||
| 第276行: | 第278行: | ||
CONFIG_USB_DWC2_VERBOSE=y | CONFIG_USB_DWC2_VERBOSE=y | ||
CONFIG_USB_DWC2_DEBUG_PERIODIC=y | CONFIG_USB_DWC2_DEBUG_PERIODIC=y | ||
| − | + | DWC2驱动程序的调试支持(CONFIG_USB_DWC2_DEBUG)编译位于Linux内核{{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/usb/dwc2/}} 文件夹。<br/> | |
| − | {{Info| | + | {{Info|提醒:需要通过控制台使用引导参数或“ dmesg -n 8”命令将“ loglevel”增加到8}} |
| − | + | DWC2驱动程序还会导出包含有用信息的debugfs条目: | |
{{Board$}} ls /sys/kernel/debug/49000000.usb-otg/ | {{Board$}} ls /sys/kernel/debug/49000000.usb-otg/ | ||
dr_mode ep0 ep1in ep1out ep2in ep2out ep3in ep3out ep4in ep4out ep5in ep5out ep6in ep6out ep7in ep7out ep8in ep8out fifo hw_params params regdump state testmode | dr_mode ep0 ep1in ep1out ep2in ep2out ep3in ep3out ep4in ep4out ep5in ep5out ep6in ep6out ep7in ep7out ep8in ep8out fifo hw_params params regdump state testmode | ||
| − | * '''dr_mode''' | + | * '''dr_mode''' 表示USB控制器的工作模式。 它可以是“主机”,“外围设备”或“ otg”。 该值是通过设备树属性设置的。 |
| − | * '''ep*''' | + | * '''ep*''' 文件显示给定端点的状态。 |
| − | * '''fifo''' | + | * '''fifo''' 显示了整个FIFO和所有定期发送FIFO的FIFO信息。 |
| − | * '''hw_params''' | + | * '''hw_params''' 显示了从USB控制器寄存器读取的参数。 |
| − | * '''params''' | + | * '''params''' 显示驱动程序使用的参数。 |
| − | * '''regdump''' | + | * '''regdump''' 转储所有USB控制器寄存器。 |
| − | * '''state''' | + | * '''state''' 显示了硬件控制器的总体状态以及有关可用端点的一些常规信息。 |
| − | * '''testmode''' | + | * '''testmode''' 显示/设置USB测试模式(“ test_j”,“ test_k”,“ test_se0_nak”,“ test_packet”,“ test_force_enable”)。 |
==Source code location== | ==Source code location== | ||
| − | + | 源文件位于Linux内核内部。 | |
| − | * | + | * “ USB框架”位于{{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/usb/}} |
| − | * | + | * 用于 [[USBH internal peripheral | STM32 USBH]]的驱动位于 {{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/usb/host/ehci-platform.c}}, {{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/usb/host/ehci-hcd.c}} and {{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/usb/host/ohci-platform.c}}, {{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/usb/host/ohci-hcd.c}} |
| − | * | + | * 用于 [[OTG internal peripheral | STM32 OTG]]的驱动位于{{CodeSource | Linux kernel | drivers/usb/dwc2/}} |
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
2020年11月10日 (二) 11:41的最新版本
本文提供有关 Linux® USB框架的信息
它举例说明了如何激活USB接口,以及如何从用户空间访问它。
目录
Framework purpose
USB(通用串行总线)Linux®框架支持多种类型的:
- 主机控制器和外围设备
- 在外围设备中使用的小工具驱动程序和类
Linux可以在主机上使用。 在这种情况下,可以插入各种类型的外围设备,例如:
- 大容量存储(硬盘驱动器,USB记忆棒..)
- HID(键盘,鼠标..)
使用小工具驱动程序,Linux也可以用作外围设备。 在这种情况下,它可以充当:
- USB大容量存储(例如,导出某些分区,文件系统)
- 以太网卡
- 串口
- ...
System overview
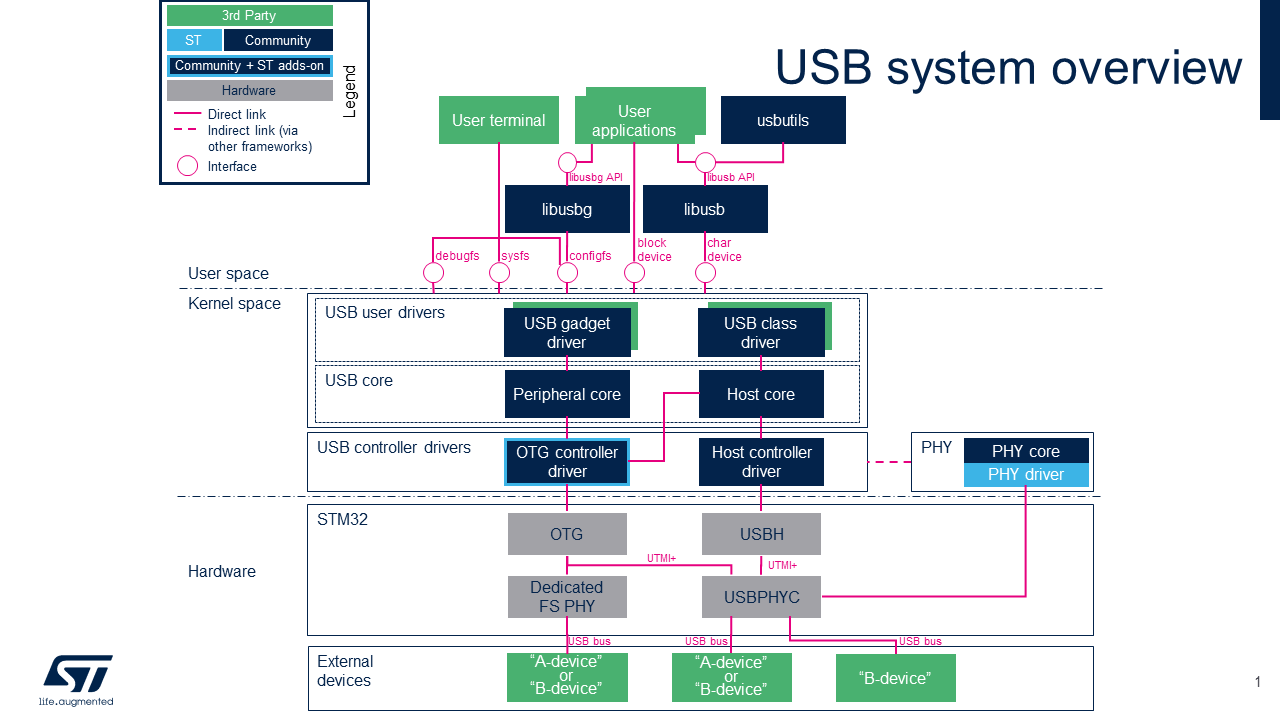
Component description
-
USB用户空间('用户空间)
- “Host-Side”用户区
- - libusb[1]是一个Userland库,可提供对USB设备的访问。
- - usbutils[2] 是一组USB实用程序,用于收集有关连接到USB主机的USB设备的信息。 注意usbutils取决于libusb。
- - 众所周知的实用程序之一是lsusb,它用于显示有关USB总线及其连接的设备的信息。
- Gadget 用户群
- - libusbg[3] 是一个Userland库,它提供了使用configfs API创建和解析USB小工具设备的例程。
- - |}} Gadget configfs 提供通过用户终端可用的配置界面,用于配置USB小工具。
- 公共用户区
- - 'sysfs提供了一个可通过用户终端使用的信息界面。 请参见 How to monitor with sysfs below.
- - debugfs提供了一个调试界面,可通过用户终端使用。 请参见 How to monitor with debugfs .
-
USB framework (内核空间): 由两部分组成,即USB“主机侧”和USB“小配件”,它们依赖于具有特定 APIs 以支持USB主机和设备控制器
- 主机端为类驱动程序提供API接口,并将请求从类驱动程序转发到主机控制器驱动程序。
- Gadget需要外围控制器和小工具驱动程序才能使用。
-
USB controller drivers (内核空间)
- USB Host-Side框架中的“ USB Host控制器驱动程序”,例如 STM32 USBHUSB Host控制器。 STM32 USBH 基于USB framework使用内核社区驱动程序(内核空间)。
- - |}} Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI) driver and |}} Generic platform ehci driver
- - |}} Open Host Controller Interface (OHCI) driver and |}} Generic platform ohci driver
- USB Host-Side框架中的[USB OTG控制器驱动程序,例如 STM32 OTG USB OTG控制器,如果在'otg或host中使用它们 ”和/或USB小工具框架中的“ otg”或“ peripheral”模式使用。STM32 OTG 基于USB framework使用内核社区驱动程序(内核空间)
- USB控制器驱动程序可以依靠 Generic PHY framework 管理USB数据传输的物理层。 STM32 USBPHYC PHY提供程序是通用PHY框架中的“ PHY驱动程序”:
- USB hardware controllers (硬件)
USB控制器,例如 STM32 USBH internal peripheral和 STM32 OTG internal peripheral, 使用片上高速UTMI + PHY(STM32 USBPHYC internal peripheral)),或用于STM32 OTG internal peripheral的片上全速PHY。
-
USB devices (外部USB设备)
- USB OTG规范[4]为USB设备定义了两个角色:A设备和B设备。 STM32 OTG controller取决于所使用的USB连接器,可以同时接受A设备和B设备,而 STM32 USBH Host controller 仅管理B设备 :
- - A-Device是一个充当USB主机的电源供应商(例如PC)
- - B-device是耗电量,充当USB外设(例如,USB闪存盘)。
API description
有关API函数的更多详细信息,请参见USB kernel documentation 。
Configuration
Kernel configuration
在ST交付中,默认情况下激活USB支持,STM32 USBH 驱动程序和STM32 OTG 驱动程序。 但是,如果需要特定的配置,则本节说明如何在内核中激活/停用USB框架。 使用Linux Menuconfig工具在内核配置中激活USB支持(CONFIG_USB=y):Menuconfig or how to configure kernel 然后选择:
Device Drivers ---> [*] USB support --->
然后激活USB控制器驱动程序。
要激活 STM32 USBH 驱动程序,请选择:
Device Drivers ---> --- USB support <*> Support for Host-side USB <*> EHCI HCD (USB 2.0) support <*> Generic EHCI driver for a platform device <*> OHCI HCD (USB 1.1) support <*> Generic OHCI driver for a platform device
要激活 STM32 OTG 驱动程序,请选择:
Device Drivers --->
--- USB support
<*> Support for Host-side USB
<*> USB Gadget Support --->
<*> DesignWare USB2 DRD Core Support
DWC2 Mode Selection (Dual Role mode) --->
然后,要激活STM32 USBPHYC 驱动程序,请选择:
PHY Subsystem ---> -*- PHY Core <*> STMicroelectronics STM32 USB HS PHY Controller driver
Device tree configuration
STM32 USB内部外围设备的详细DT配置:
How to use the framework
How to list USB devices
lsusb显示有关所连接的USB总线和设备的信息。
在上面的示例中,我们有一个板载集线器,一个USB鼠标和USB键盘插入了该集线器。
Board $> lsusb /* root hubs correspond to STM32 USB controllers (USBH, OTG) */
Bus 002 Device 005: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard
Bus 002 Device 004: ID 046d:c016 Logitech, Inc. Optical Wheel Mouse
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Bus 002 Device 002: ID 0424:2514 Standard Microsystems Corp. USB 2.0 Hub
Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Board $> lsusb -t /* lsusb -t shows the USB class, the driver used and the number of ports and speed of each USB devices */
/: Bus 02.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=ehci-platform/2p, 480M
|__ Port 1: Dev 2, If 0, Class=Hub, Driver=hub/4p, 480M
|__ Port 1: Dev 5, If 0, Class=Human Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 1.5M
|__ Port 3: Dev 4, If 0, Class=Human Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 1.5M
/: Bus 01.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=dwc2/1p, 480M
要将lsusb限制为USB键盘:
Board $> lsusb -s 002:005 /* lsusb -s [Bus]:[Device] */ Bus 002 Device 005: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard Board $> lsusb -d 413c:2003 /* lsusb -d [ID] */ Bus 002 Device 005: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard
要将lsusb限制为USB键盘并显示其描述符:
Board $> lsusb -D /dev/bus/usb/002/005 /* lsusb -D /dev/bus/usb/[Bus]/[Device] */
Device: ID 413c:2003 Dell Computer Corp. Keyboard
Device Descriptor:
...
How to mount a USB key (mass-storage)
Board $> mkdir /usb Board $> mount /dev/sdxx /usb
How to configure USB Gadget through configfs
请参阅USB gadget configfs documentation ,以获取USB gadget configfs结构的介绍以及如何使用它来配置Linux USB Gadget。
以下是通过配置文件配置USB Gadget以将OTG用作具有远程NDIS(RNDIS)的USB以太网Gadget的示例。 见: stm32_usbotg_eth_config.sh.
How to trace and debug the framework
How to monitor
How to monitor with debugfs
请参考the USB devices chapter[5] 对输出进行解码。
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/devices T: Bus=01 Lev=00 Prnt=00 Port=00 Cnt=00 Dev#= 1 Spd=480 MxCh= 1 B: Alloc= 0/800 us ( 0%), #Int= 0, #Iso= 0 D: Ver= 2.00 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=01 MxPS=64 #Cfgs= 1 P: Vendor=1d6b ProdID=0002 Rev= 4.14 S: Manufacturer=Linux 4.14.0 dwc2_hsotg S: Product=DWC OTG Controller S: SerialNumber=49000000.usb-otg C:* #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=e0 MxPwr= 0mA I:* If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 1 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=00 Driver=hub E: Ad=81(I) Atr=03(Int.) MxPS= 4 Ivl=256ms T: Bus=01 Lev=01 Prnt=01 Port=00 Cnt=01 Dev#= 4 Spd=480 MxCh= 0 D: Ver= 2.00 Cls=00(>ifc ) Sub=00 Prot=00 MxPS=64 #Cfgs= 1 P: Vendor=05e3 ProdID=0723 Rev=94.54 S: Manufacturer=Generic S: Product=USB Storage C:* #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=80 MxPwr=500mA I:* If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 2 Cls=08(stor.) Sub=06 Prot=50 Driver=usb-storage E: Ad=81(I) Atr=02(Bulk) MxPS= 512 Ivl=0ms E: Ad=02(O) Atr=02(Bulk) MxPS= 512 Ivl=0ms T: Bus=02 Lev=00 Prnt=00 Port=00 Cnt=00 Dev#= 1 Spd=480 MxCh= 2 B: Alloc= 0/800 us ( 0%), #Int= 2, #Iso= 0 D: Ver= 2.00 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=00 MxPS=64 #Cfgs= 1 P: Vendor=1d6b ProdID=0002 Rev= 4.14 S: Manufacturer=Linux 4.14.0 ehci_hcd S: Product=EHCI Host Controller S: SerialNumber=5800d000.usbh-ehci C:* #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=e0 MxPwr= 0mA I:* If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 1 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=00 Driver=hub E: Ad=81(I) Atr=03(Int.) MxPS= 4 Ivl=256ms T: Bus=02 Lev=01 Prnt=01 Port=00 Cnt=01 Dev#= 2 Spd=480 MxCh= 4 D: Ver= 2.00 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=02 MxPS=64 #Cfgs= 1 P: Vendor=0424 ProdID=2514 Rev= b.b3 C:* #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=e0 MxPwr= 2mA I: If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 1 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=01 Driver=hub E: Ad=81(I) Atr=03(Int.) MxPS= 1 Ivl=256ms I:* If#= 0 Alt= 1 #EPs= 1 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=02 Driver=hub E: Ad=81(I) Atr=03(Int.) MxPS= 1 Ivl=256ms T: Bus=02 Lev=02 Prnt=02 Port=03 Cnt=01 Dev#= 5 Spd=1.5 MxCh= 0 D: Ver= 1.10 Cls=00(>ifc ) Sub=00 Prot=00 MxPS= 8 #Cfgs= 1 P: Vendor=413c ProdID=2003 Rev= 1.00 S: Manufacturer=Dell S: Product=Dell USB Keyboard C:* #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=a0 MxPwr= 70mA I:* If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 1 Cls=03(HID ) Sub=01 Prot=01 Driver=usbhid E: Ad=81(I) Atr=03(Int.) MxPS= 8 Ivl=24ms
How to monitor with sysfs
USB buses monitoring with sysfs
请参考What are the sysfs structures for Linux USB?[6].
Board $> ls /sys/bus/usb/devices/ 1-0:1.0 1-1 1-1:1.0 2-0:1.0 2-1 2-1.4 2-1.4:1.0 2-1:1.0 usb1 usb2
以“usb''开头的名称是指USB控制器。
设备命名方案如下:
- bus-port.port.port... (1-1, 2-1, or 2-1.4 in the example above)
这些接口由后缀表示,格式如下:
- :config.interface (1-1:1.0, 2-1:1.0, 2-1.4:1.0 in the example above)
每个接口对应于sysfs中的一个条目,并且可以具有自己的驱动程序。
USB Gadget monitoring with sysfs
配置USB小工具后,将填充USB设备控制器sysfs。 参见 Documentation/ABI/stable/sysfs-class-udc| |}} Documentation/ABI/stable/sysfs-class-udc for a description of each file.
Board $> ls /sys/class/udc/49000000.usb-otg/ a_alt_hnp_support device is_selfpowered srp a_hnp_support function maximum_speed state b_hnp_enable is_a_peripheral power subsystem current_speed is_otg soft_connect uevent
How to trace
How to trace with usbmon
usbmon [7] 收集USB总线上的输入/输出轨迹。
它依赖于内核部分和用户部分,并将USB设备驱动程序发出的请求报告给主机控制器驱动程序。
使用Linux Menuconfig工具在Menuconfig or how to configure kernel内核配置中激活USBMON支持(CONFIG_USB_MON = y)。
在debugfs中创建了一个usbmon条目。 它包括几个文件。
文件名由一个数字(USB总线-0表示所有总线)和一个字母(s,u或t)组成。 s文件包含通用事件概述。 t(不建议使用)和u文件将流跟踪数据。
要收集调试数据,请使用主文件0u(以从所有设备捕获数据)或找出设备所连接的总线并使用相应的总线文件。 例如,如果设备连接到总线1:
Board $> cat /sys/kernel/debug/usb/usbmon>1u > bus1data.log
要停止捕获,只需键入(CTRL + C)即可终止命令。 然后,您可以使用Linux主机上的 vUSBAnalyzer 图形工具来分析日志
How to trace using a protocol analyzer
USB协议分析器是一种USB流量嗅探器,用于解码USB描述符并显示发送的总线状态和数据包。 请参阅您的USB协议分析器用户手册。
How to debug
Activating USB framework debug messages
有关详细的动态跟踪信息,请参阅 How to use the kernel dynamic debug
Board $> echo "file usb* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
此命令在运行时启用与USB内核和驱动程序相关的所有跟踪。
通过仅选择要跟踪的文件,可以进行更精细的选择。
| 提醒:loglevel需要通过使用引导参数或从控制台发送dmesg-n 8命令增加到8 |
EHCI/OHCI driver debugfs entry
启用CONFIG_DYNAMIC_DEBUG时,EHCI/uchI驱动程序会导出调试文件系统条目。
Board $> ls /sys/kernel/debug/usb/ohci/5800c000.usbh-ohci/ 异步周期寄存器 Board $> ls /sys/kernel/debug/usb/ehci/5800d000.usbh-ehci/ 异步带宽定期寄存器
- async 转储异步计划的快照。
- bandwith 转储带宽分配
- periodic 转储定期计划的快照。
- registers 转储USB控制器寄存器
DWC2 driver debug messages and debugfs entry
要从 STM32 OTG,通过menuconfigMenuconfig or how to configure kernel在Linux内核中激活“启用调试消息”。
Device Drivers ---> [*] USB support <*> Support for Host-side USB <*> USB Gadget Support ---> <*> DesignWare USB2 DRD Core Support [*] Enable Debugging Messages [*] Enable Verbose Debugging Messages [ ] Enable Missed SOF Tracking [*] Enable Debugging Messages For Periodic Transfers
这可以在您的内核.config文件中手动完成:
CONFIG_USB_SUPPORT=y CONFIG_USB_DWC2=y CONFIG_USB_DWC2_DEBUG=y CONFIG_USB_DWC2_VERBOSE=y CONFIG_USB_DWC2_DEBUG_PERIODIC=y
DWC2驱动程序的调试支持(CONFIG_USB_DWC2_DEBUG)编译位于Linux内核drivers/usb/dwc2/| |}} drivers/usb/dwc2/ 文件夹。
| 提醒:需要通过控制台使用引导参数或“ dmesg -n 8”命令将“ loglevel”增加到8 |
DWC2驱动程序还会导出包含有用信息的debugfs条目:
Board $> ls /sys/kernel/debug/49000000.usb-otg/ dr_mode ep0 ep1in ep1out ep2in ep2out ep3in ep3out ep4in ep4out ep5in ep5out ep6in ep6out ep7in ep7out ep8in ep8out fifo hw_params params regdump state testmode
- dr_mode 表示USB控制器的工作模式。 它可以是“主机”,“外围设备”或“ otg”。 该值是通过设备树属性设置的。
- ep* 文件显示给定端点的状态。
- fifo 显示了整个FIFO和所有定期发送FIFO的FIFO信息。
- hw_params 显示了从USB控制器寄存器读取的参数。
- params 显示驱动程序使用的参数。
- regdump 转储所有USB控制器寄存器。
- state 显示了硬件控制器的总体状态以及有关可用端点的一些常规信息。
- testmode 显示/设置USB测试模式(“ test_j”,“ test_k”,“ test_se0_nak”,“ test_packet”,“ test_force_enable”)。
Source code location
源文件位于Linux内核内部。
- “ USB框架”位于drivers/usb/| |}} drivers/usb/
- 用于 STM32 USBH的驱动位于 drivers/usb/host/ehci-platform.c| |}} drivers/usb/host/ehci-platform.c , drivers/usb/host/ehci-hcd.c| |}} drivers/usb/host/ehci-hcd.c and drivers/usb/host/ohci-platform.c| |}} drivers/usb/host/ohci-platform.c , drivers/usb/host/ohci-hcd.c| |}} drivers/usb/host/ohci-hcd.c
- 用于 STM32 OTG的驱动位于drivers/usb/dwc2/| |}} drivers/usb/dwc2/
References
- ↑ libusb: a cross-platform library to access USB devices
- ↑ usbutils: USB utilities for Linux, including lsusb
- ↑ libusbg: a C library encapsulating the kernel USB gadget-configfs userspace API functionality
- ↑ On-The-Go and Embedded Host Supplement to the USB Revision 2.0 Specification
- ↑ Linux USB API: The Linux-USB Host Side API - The USB devices
- ↑ What are the sysfs structures for Linux USB?
- ↑ Documentation/usb/usbmon.txt | |}} usbmon